Boston Industrial Solutions, Inc., has the best pad printing ink lines for printing any application. Our silicone, UV ink, and solvent-based pad printing inks are safe and fade-resistant. Furthermore, we rigorously test these inks to exceed demanding industry standards for performance, adhesion, and compliance. These pad printing inks are excellent for printing different types of applications, including promotional, apparel, consumer electronics, drinkware, sporting goods, silicone rubber, cosmetic packaging, toys, and more.
The Natron® pad printing inks portfolio has medical-grade, high-abrasion, chemical-resistance, dishwasher-safe, and high-density inks. Additionally, we offer in-house custom color matching and ink mixing services. Other ink services that we offer include ink adhesion testing, pad printing training, and custom ink formulation. All these services are available for inkjet, pad printing, and screen-printing inks.
Learn more about the Natron® pad printing inks, how to choose the best ink for your application, and more.

Pad printing ink is a special type of “paint” formulated for application using a pad printing machine to a substrate as a thin ink film (print) that dries quickly. Ink manufacturers combine solvents and solid matter to create the ink. The solid matter includes binders, resins, additives, catalysts, photo initiators, and pigments. The specific formulation of pad printing ink will vary depending on the application, substrate, compliance, and environmental considerations.
The pad printing process is an indirect printing process where a silicone pad transfers a thin film of ink as a 2D image from an engraved plate (cliché) onto a 3D object.
The formula for making pad printing ink is: (solids + solvent = pad printing ink). Where solid matter = binders + resins + other additives. The type and ratio of these components will vary depending on the type of ink.


There are several types of ink for pad printing. These are solvent-based ink, UV-curable ink, silicone ink, and water-based ink. Many industries widely use solvent-based inks, which are the most common.
Furthermore, there are two types of pad printing inks: one-component inks and two-component inks.
Lastly, pad printing inks are further classified based on the substrates they adhere to. E.g., ink for metals, plastics, glass, silicone, cotton, etc.
Boston Industrial Solutions, Inc., manufactures and provides pad printing ink for almost all possible substrates and applications. Examples of pad printing applications include medical devices, cosmetic packaging, automotive parts, promotional items, toys, sporting goods, appliances, consumer electronics, and more. We will cover solvent-based inks and silicone inks in detail below.
Solvent-based pad printing ink is the most common type of ink used in the pad printing process. These inks use solvent as the base and carrier of the ink. The solvent allows the ink to easily print, spread, and transfer during the pad printing process. Because these inks use solvents, they have a volatile organic compound (VOC) component that varies from one ink to another. After printing, the solvent evaporates, leaving the pigment, resin, and binders, also known as the solids, on the substrate.

The chemical components of pad printing ink vary depending on the specific ink formulation and the ink’s intended use. The most important components used to make pad printing ink include binders, resins, solvents (thinners), and pigments (colorants).
In this section, we will examine each of the parts that make up pad printing ink in detail.
Generally, the solvent (thinner) is typically 10–65% of the ink composition. The solvent in pad printing ink serves several purposes. Pigment (color dispersion) is one of the critical roles of solvent during ink formulation. Solvents evenly suspend the pigments within the ink.
Maintaining the ink viscosity (thickness of the ink) is another important function of the solvent base.
The solvent also plays a critical role in drying and curing the ink. The quick-drying feature is important for maintaining the quality of the print. This helps prevent the ink from smudging. Except for UV inks and silicone inks, all our solvent-based pad printing inks are dry to touch in seconds to minutes after printing. This is part of the reason that it is possible to print wet on wet or a 4-color process with pad printing or screen-printing machines.
The bonding of the ink with the substrate is another function of the solvent base. The solvent helps with the ink bonding with the base material.
Lastly, different substrates have different surface and chemical properties. The choice of solvent in pad printing ink manufacturing is critical to matching the different substrates. Solvents make it possible for one ink to print effectively across multiple substrates.


Both binders and resins play a critical role in pad printing ink formulation. These two components are different, although many ink suppliers use these terms interchangeably. Let’s explore the differences between resins and binders.
Binders constitute 15 to 50% of the composition of the ink. Binders wet the pigment, which facilitates the dispersion of its particles. As a result, binders hold the pigments together, hence creating a consistent and uniform layer of ink on the printed surface. Examples of polymers include acrylics, vinyl, polyurethane, etc. These materials form the adhesion and flexibility properties of the ink. Binders contribute to the ink’s resistance to weather elements, abrasion, moisture, and chemicals.
Resins contribute to the ink’s durability and adhesion, just like binders. Also, they act as a protective barrier and add to the finish (gloss or matte finish) characteristics of the printed image. Most people confuse binders and resins because they have similar polymers.
Lastly, binders and resins act as the adhesive that determines the printing properties of the ink as well as the way it bonds with the substrate.
Pigments (colorant substances) constitute 5–30% of ink. We triple-mill the pigments to achieve very fine particles. Next, we disperse these finely milled solid substances in the binder.
Color and opacity are the primary functions of pigments in pad printing ink formulation. Color is the desired hue (shade), whether it’s a standard color, metallic shade, process color, neon (fluorescent) color, or a custom color. Opacity refers to the ink’s transparent characteristics. High-opaque ink ensures that the printed image completely covers and conceals (hides) the underlying substrate, maintaining the ink’s color integrity.
Other functions of pigments include:

Silicone ink is a type of screen and pad printing ink that consists of silicone polymers and silicone ink concentrates (pigments) for printing on silicone rubber applications. Additionally, these inks are 2-component inks; for this ink to function, a catalyst (platinum-based) and a thinner (solvent) are required. Silicone inks require heat to dry and cure. However, it is possible to print on other materials, such as glass and metal, using our Citrine® silicone primers.
Lastly, once cured, silicone ink is the only type of print that can stretch, bend, and move with silicone, as well as withstand high temperatures. Once fully cured, silicone ink will hold up to anything silicone can.
Now that you understand the various components of pad printing ink, next we will review the ink’s characteristics. In pad printing, there is no one ink that prints and adheres to all substrates. The different resins, binders, etc. result in creating inks that have different qualities. However, the different inks share common characteristics. These common characteristics are ink durability, adhesion, drying speed, color range, and opacity.


There are several important documents to review to ensure that the pad printing process is carried out safely and in compliance with relevant standards. These datasheets include safety data sheets, technical data sheets, standard operating procedures, etc. We will review the importance of technical data sheets (TDS).
As discussed, pad printing uses one- or two-component solvent-based ink, UV ink, or silicone-based ink. Different inks use different additives and adhere to different substrates. For this reason, it is important to consult the technical data sheet for each ink to determine what ink is suitable for your printing application. A technical data sheet is a specification sheet for a product. It summarizes the technical characteristics of the product and gives the user a full understanding of what and how to use a specific product. Therefore, it is important to review the TDS for each ink before using it.
In a technical data sheet, you will learn:
There are various factors to consider when choosing the best pad printing ink for your application. Here are the most important factors to consider when choosing ink for your printing application:


Pad printing additives are substances added to the inks to enhance various characteristics of the ink properties, such as adhesion, drying time, viscosity, and flexibility. Some common types of additives include thinners (solvents), retarders, thickeners, hardeners, adhesion promoters, anti-static paste, matting agents, anti-skinning agents, and flow agents.
Let us review two of the most common types of pad print ink additives: hardener and thinner.
Different pad printing inks dry at different speeds. For solvent-based inks, the printed ink film takes about 24 hours to dry and about 76 hours to achieve full cure. On the other hand, UV inks dry instantly on exposure to UV light at 395nm. UV inks take about 24 hours to achieve full cure. While silicone inks will eventually air dry, heat is required to speed up drying time.
The amount of hardener (catalyst) used affects the rate at which the printed image dries. Moreover, the use of faster-evaporating solvents will increase the rate at which the ink film dries.
Consider using heat tunnels to speed up the drying process of the ink. Except for silicone, after heating the substrate, other inks still require a 24-hour period to achieve full cure. Silicone inks cure immediately after the heated silicone product cools down.
Lastly, on average, it takes about 25 seconds for most solvent-based pad printing inks to achieve “dry-to-touch” status.


At Boston Industrial Solutions, Inc., we offer inks to many industries and for printing on many types of materials and applications. Some of the industries that use our inks include:
Every ink that Boston Industrial Solutions, Inc. manufactures and supplies conforms to the most stringent worldwide standards, such as EuPIA, GADSL, RoHS, EN 71/3, REACH, USP Class VI, cGMP, GAMP5, and FDA.
The scientific and manufacturing industries are always coming up with new materials. For this reason, it might not be possible to have ink to print on all substrates. However, for the most challenging applications, with the combination of adhesion promoters, it is possible to print on almost all materials. Boston Industrial Solutions, Inc. offers different types of inks for printing on almost any kind of material that you can think of, such as:


Ink mixing is an interchangeable term for ink color matching. Over the years, Boston Industrial Solutions, Inc., has developed a large library of colors. We store these colors in our color-matching system. These colors are available for all our pad printing ink ranges.
If a color is not available, following the RAL, PMS, or HEX system, we can formulate any color that you can dream of. We use advanced tools such as spectrophotometers to accurately calculate and match the ratios needed for a perfect color match. We match inks to perfectly print nearly any shade on any printable substrate background, dark or light.
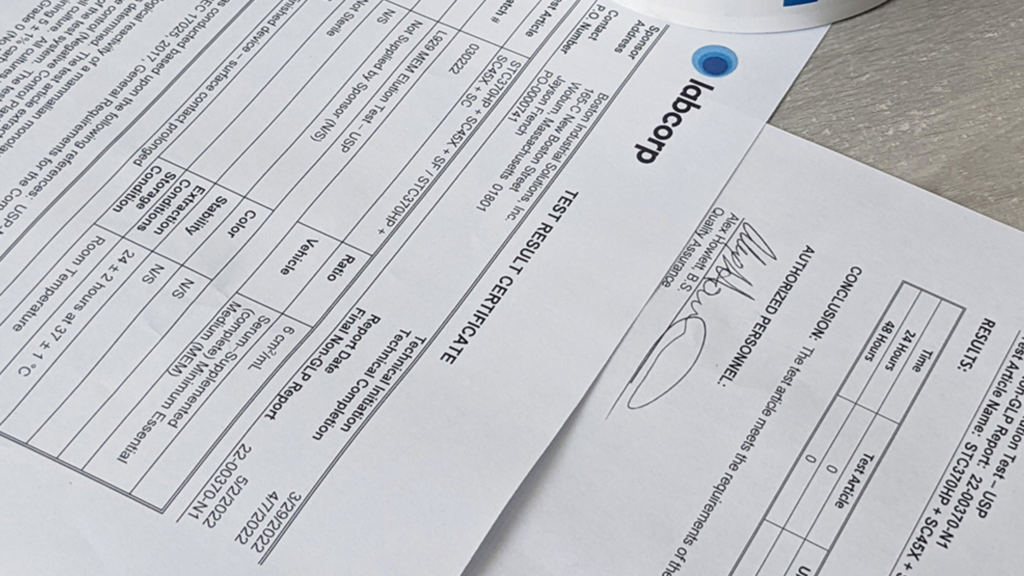
Adhesion testing is an important part of the development and quality control of pad printing. Adhesion testing ensures that printed images meet customer-required standards for durability and longevity. Additionally, it helps identify potential problems in pre-production.
At Boston Industrial Solutions, Inc., we offer ink adhesion testing following the ASTM industry standards.

There are very many industries that use pad printing inks for marking, printing, and decorating products. Many people use these products daily. As a result, it is very important that inks comply with various standards.
The reasons for compliance include product safety, consumer protection, environmental impact, worker health and safety, legal requirements, global markets, quality, supply chain management, and ethical considerations.
The most common compliance and certifications for pad printing inks include RSL, CPSIA, EuPIA, GADSL, RoHS, EN 71/3, REACH, USP Class VI, cGMP, GAMP5, and FDA.
All our printing inks do not contain heavy metals (lead, cadmium, mercury) or phthalates. In addition, some of our inks, such as the SE-F, MG, and BX series, are Class IV certified. This means that these inks meet strict medical safety standards.
For pad printing on textiles, important certification includes Eco Passport by Oeko-Tex®. This compliance testing checks for chemicals, colorants, and auxiliaries used to manufacture textiles. It checks inks for human skin contact. The ST Series ink for tagless printing on apparel ensures no exposure to toxic chemicals when prints come into contact with human skin. Since these tags are touching skin for prolonged periods of time daily, it is essential that there be no exposure to toxic chemicals.
Specifications are requirements by the end user that pad printing inks have specific characteristics and meet certain standards. For example, Military (MIL-Spec)/Aerospace Qualified Ink-Military spec to MIL-I-43553 and AA56032. When properly applied and cured, the ink has excellent adhesion to metal, glass, and hard plastics. The ink is resistant to acids, alkalies, solvents, salt spray, and thermal shock. The Natron MG Series ink for glass, metals, ceramics, and hard plastics meets military specifications for MIL-I-43553 and AA56032. This printing ink is a permanent, two-component, epoxy-based printing ink. Use the i-240x hardener, which cures at elevated and/or room temperatures. For room-temperature curing, perform adhesion testing 18–36 hours after printing. This waiting time enables the ink to cross-link to the substrate. In some cases, the printed product can take up to 6 days to achieve full cure.
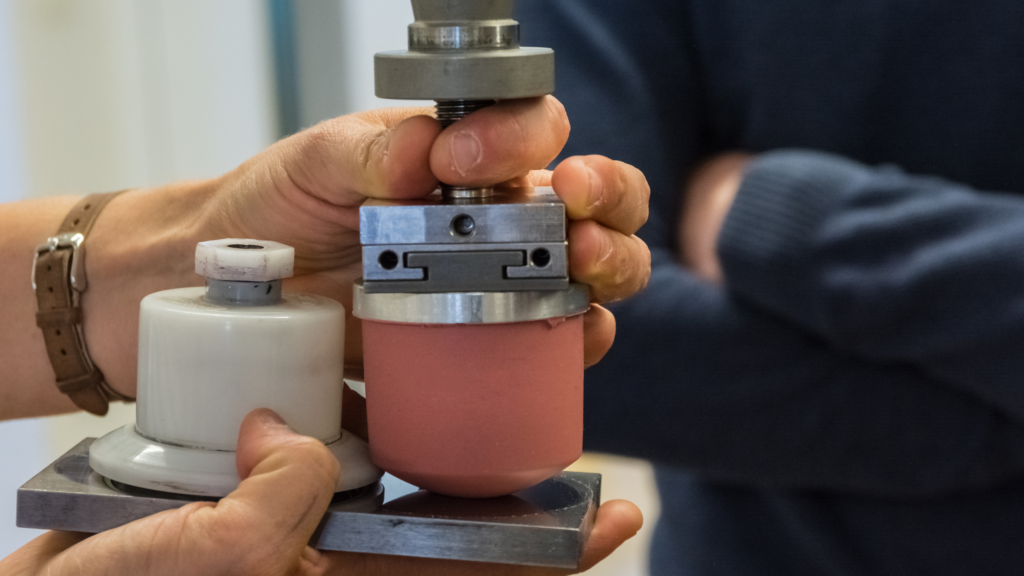

Like any other printing method, there are certain pad printing ink-related problems that may affect the quality of the prints. It is therefore important to identify and address these issues to achieve consistent printing results. Here are some common ink problems during pad printing:
Poor ink adhesion, ink bleeding (leaking from the cup), ink smearing, ink drying too quickly, ink contamination, ink not transferring properly, ghosting, and ink curing issues. Visit our support hub for more information.
As we conclude, let’s review concerns and new developments in pad printing ink. The current concerns include:
Most of the new developments in the pad printing industry are sustainability-driven. The new areas of development include:


For more information on our pad printing inks, check out the Pad Printing Ink Overview on our blog.