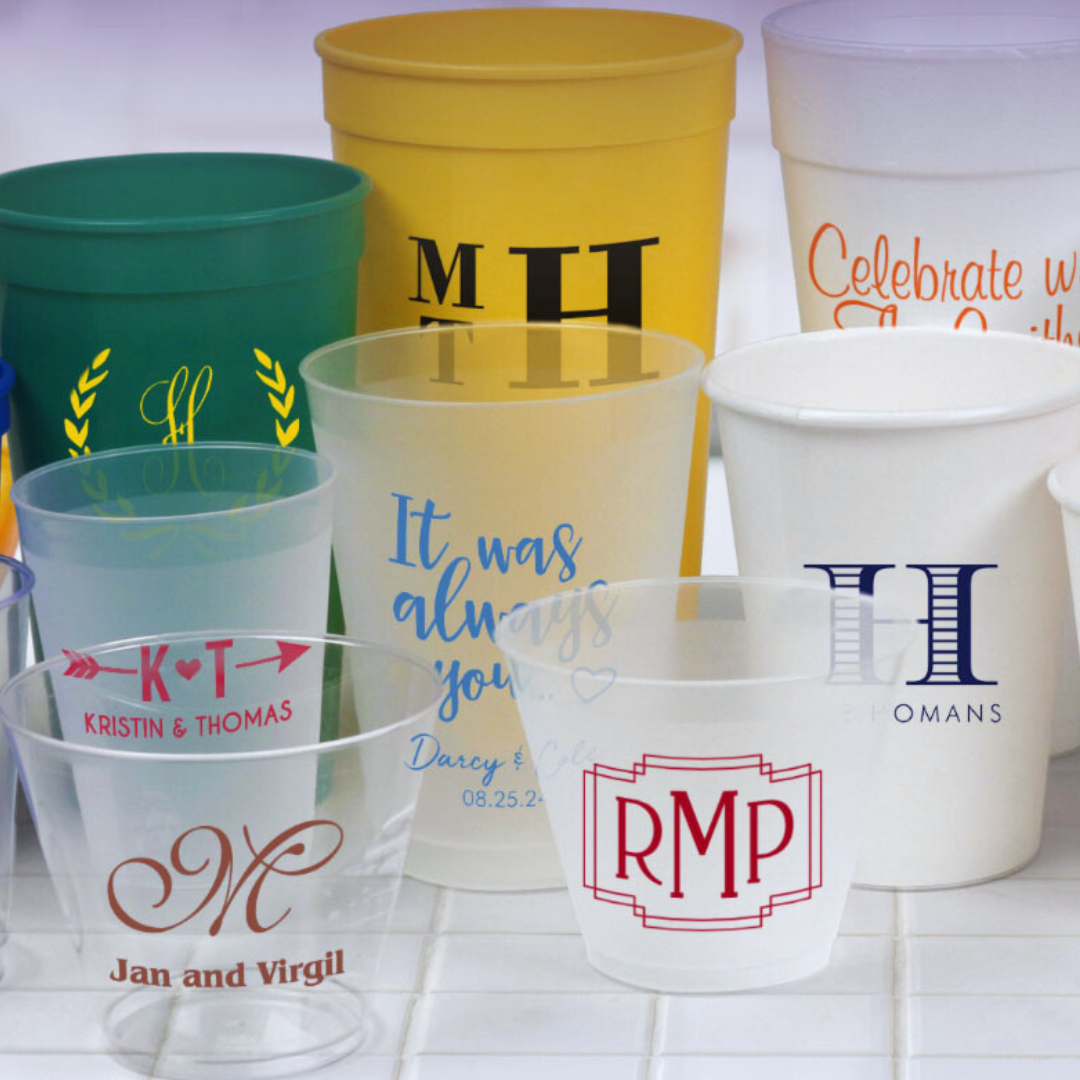
What are the best screen printing ink for plastic cups.
Promotional products, such as branded cups, generate over 3,000 impressions during their lifetime. Additionally, 90% of consumers own more than one branded cup. For these reasons, it is important for businesses to embrace plastic-printed cups to advertise their brands. However, to achieve the best imprints, it is important to use the right type of screen printing ink for plastic cups. In this article, we will discuss the best screen printing ink options for plastic cups.
Types of screen printing inks for cups
There are two types of ink for screen printing on plastic cups. These are solvent-based and UV-based screen printing inks. UV printing inks use ultraviolet light to dry the inks, whereas solvent inks dry via evaporation or heat. It is important to note that there are other major differences between these two inks, such as environmental impact and ink composition. We will not focus on these differences in this article.
UV printing inks.
Many contract printers are adapting UV inks for printing on plastic cups due to their durability, efficiency, and sustainability features. When exposed to ultraviolet light, these inks dry instantly. It is, however, important to note that the ink’s curing time takes 24 to 48 hours after the ink film is exposed to UV light. The image results in a durable and long-lasting print.
Also, UV inks for screen printing on plastic cups are resistant to fading and scratching. This makes them ideal not only for single-use stadium cups but also for multiple-use cups.
PET, or polypropylene, material forms the basis of many cups. It is important to note that pre-treatment options are required for inks to adhere to PET (PE) and polypropylene plastics. Two types of pre-treatments are available: mechanical and chemical. Chemical pre-treatment includes PP primer, whereas mechanical systems include pryosil and flame treatment. Lastly, UV inks are available in a wide range of colors, allowing you to create eye-catching designs for your branded cups. Learn more about our Natron® pad printing ink.
Solvent-based inks
Solvent-based inks are a popular choice for printing on plastic cups. These inks will dry on screens, unlike UV inks, which remain wet until exposed to UV light. To solve this problem, we use a retarder solvent to slow down the evaporation rate.
Boston Industrial Solutions, Inc. makes many different types of solvent inks. Our inks are known for their ease of use, ability to bond to many different plastics, and durability. Furthermore, these inks are resistant to detergents and numerous other chemicals. As a result, these inks are an excellent choice for cups used outdoors or in high-abrasion environments.
The MG Series, the EK Series, and the TP Series are examples of screen-printed inks for cups. Learn more about the best inks for screen printing cups.
Lastly, like UV inks, polyproylene cups require pre-treatment prior to printing. Learn more about our UV ink adhesion promoters, which are also excellent for use with solvent-based inks.
Curing inks for screen printing on cups.
To dry UV inks, you need to use a UV curing unit. For solvent inks, a drying oven is required. It is important to make sure that you test how much heat the cups can take before putting them into the drying oven. Higher temperatures will melt the cups. If the temperature is high, adjust it to the appropriate level. Learn more about UV ink adhesion.
Advantages of using the right screen printing inks for plastic cups
The right screen printing ink for plastic cups contributes significantly to the success of custom-printed cups. The right inks will make your cups stand out and have a long-lasting imprint. Vibrant prints will ensure maximum brand exposure for your customers. If you are not sure what ink to use, please reach out to us. Our experts are always available to help you choose the right inks for your printing application. Additionally, subscribe to our YouTube channel for the latest printing news, and visit our support hub to learn more about printing.